728x90
⬛ 깊이 우선 탐색 | DFS
🟩 1번. 가장 가까운 큰 수

풀이
- 일단 입력된 n의 구성을 잘라서 ArrayLIst에 담아주고 오름차순 정렬한다.
- 오름차순 정렬해두어야 작은값부터 차례로 순회하기 때
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
/*가장 가까운 큰 수 */
class Solution {
static int answer, target;//최초 숫자 담기
static ArrayList<Integer> num;
static boolean[] visited;//방문용
static boolean flag;
static int len; //길이
//DFS
static void DFS(int lv, int number) {
if(flag == true) return;
if(lv == len) {//길이가 7까지 갔고,
if(number > target) {
answer = number;
flag = true;
}
}else {
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) {
if(!visited[i]) {
visited[i] = true;//방문처리
DFS(lv+1, number * 10 + num.get(i));
visited[i] = false;//복귀할 때 false 주고
}
}
}
}
//솔루션
public int solution(int n){
answer = 0;
target = n;//담기
num = new ArrayList<>();
flag = false;
int m =n;
while(m >0) {
int t = m % 10;
num.add(t);
m = m / 10;
}
//오름차순 정렬
Collections.sort(num);
len = num.size();
visited = new boolean[len];
DFS(0, 0);
if(flag == false) answer = -1;
return answer;
}
//main
public static void main(String[] args){
Solution T = new Solution();
System.out.println(T.solution(123));
System.out.println(T.solution(321));
System.out.println(T.solution(20573));
System.out.println(T.solution(27711));
System.out.println(T.solution(54312));
}
}
🟩 2번. 줄다리기
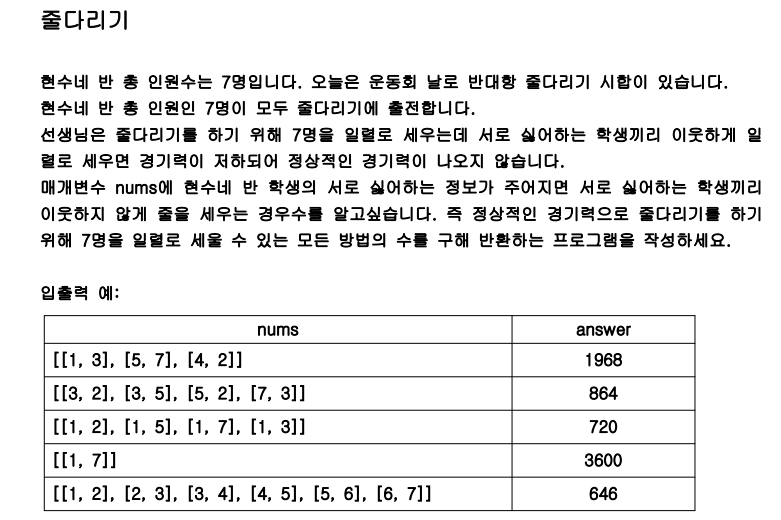
풀이
- DFS로 7명에 대한 줄 세우기를 깊이 7까지 탐색해야 하는 문제이다.
- 단 조건이 있다.
- 직전에 삽입한 번호와 relation[][] 상 이웃하지 않아야 할 번호에 대해서는 깊이 탐색 X
- 그것을 위해서 Stack을 사용하여 직전에 탐색한 번호를 후입선출 한다. 그러면 가장 직전에 방문한 애의 번호를 peek()으로 알 수 있고, 그 애를 기준으로 relation이 없고 이전에 방문 체크 되지 않은 애들에 대하여 깊이 탐색을 시도하면 된다
- 그렇게 최종 lv7 깊이까지 탐색하여 얻은 애에 대해서는 answer++ 처리하면 모든 방법의 수가 구해지는 문제이다.
/*줄다리기 문제 풀이 */
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static int answer;
static int[][] relation;//관계확인용
static boolean[] chk;//방문 체크용 배열
static Stack<Integer> stack;//여기에 직전 값 확인용
//DFS
static void DFS(int lv) {
if(lv == 7) answer++;
else {
for(int i=1; i<=7; i++) {
//직전 방문한 값과 관련있을 경우 건너뜀
if(!stack.empty() && relation[stack.peek()][i] == 1) continue;//건너뜀
if(!chk[i]) { //방문 안한 i에 대하여
chk[i] = true;//방문 체크
stack.push(i);//방문한 애 담기
DFS(lv+1);//깊이 탐색
chk[i] = false;//복귀할 때 다시 풀어주고
stack.pop();//다시 빼기
}
}
}
}
//솔루션 함수
public int solution(int[][] fight){
//초기화
answer = 0;
relation = new int[8][8];
chk = new boolean[8];
stack = new Stack<>();
for(int[] x : fight) {
relation[x[0]][x[1]] = 1;//체크
relation[x[1]][x[0]] = 1;//양쪽 다 체크
}
DFS(0);//0부터 시작
return answer;
}
//실행 메인
public static void main(String[] args){
Solution T = new Solution();
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{1, 3}, {5, 7}, {4, 2}}));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{3, 2}, {3, 5}, {5, 2}, {7, 3}}));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{1, 2}, {1, 5}, {1, 7}, {1, 3}}));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{1, 7}}));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 6}, {6, 7}}));
}
}
🟩 3번. 바둑 대회

풀이
- 두 개의 팀이 서로 겹치는 인원 없이 나뉘어야 한다.
- 따라서, lv을 n/2 까지만 돌면서 ch[] 배열로 값을 체크하고, 체크된 애는 A에 체크 안된 애는 B에 나누는 식으로 중복없이 나눈다.
- 나눈 후 sum값을 구해서 두 값의 차이 절댓값이 가장 작은 애를 answer에 누적한다.
- DFS(lv, s) 로 뻗어갈 건데 s는 시작점이다. s부터 시작해서 다음 단계로 뻗어간다.
package to_0809_3;
import java.util.*;
//바둑 대회 - DFS 조합 문제, nC2 두 팀으로 나눠서 최소 차이 나는 구성 반환
class Solution {
int n, answer;
int[] ch;
//dfs
public void DFS(int L, int s, int[][] cans){
if(L == n/2){
ArrayList<Integer> A = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> B = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(ch[i] == 1) A.add(i);
else B.add(i);
}
int Asum = 0, Bsum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < L; i++){
Asum += cans[A.get(i)][0];
Bsum += cans[B.get(i)][1];
}
answer = Math.min(answer, Math.abs(Asum - Bsum));
}
else{
for(int i = s; i < n; i++){
ch[i] = 1;
DFS(L + 1, i + 1, cans);
ch[i] = 0;
}
}
}
//solution
public int solution(int[][] cans){
answer = 1000000000;
n = cans.length;
ch = new int[n];
DFS(0, 0, cans);
return answer;
}
//main
public static void main(String[] args){
Solution T = new Solution();
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{87, 84}, {66, 78}, {94, 94}, {93, 87}, {72, 92}, {78, 63}}));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{10, 20}, {15, 25}, {35, 23}, {55, 20}}));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{11, 27}, {16, 21}, {35, 21}, {52, 21}, {25, 33},{25, 32}, {37, 59}, {33, 47}}));
}
}
728x90
'알고리즘 이론 [개념] > [개념] 코테 알고리즘 공부 - 시즌 2' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 코테 | 강의 - 너비 우선 탐색 - BFS 섹션 - (1) (0) | 2023.08.16 |
|---|---|
| 코테 | 강의 - 깊이 우선 탐색 - DFS 섹션 - (2) (0) | 2023.08.14 |
| 섹션 3. 코딩테스트 [실전편] - 11. 동적 계획법 (0) | 2023.07.11 |
| 섹션 3. 코딩테스트 [실전편] - 10. 조합 (0) | 2023.07.10 |
| 섹션 3. 코딩테스트 [실전편] - 09. 트리 - (3) 세그먼트 트리 (0) | 2023.07.10 |

