728x90
⬛ 그래프 알고리즘
🟩 1번. 최소 비행료 문제
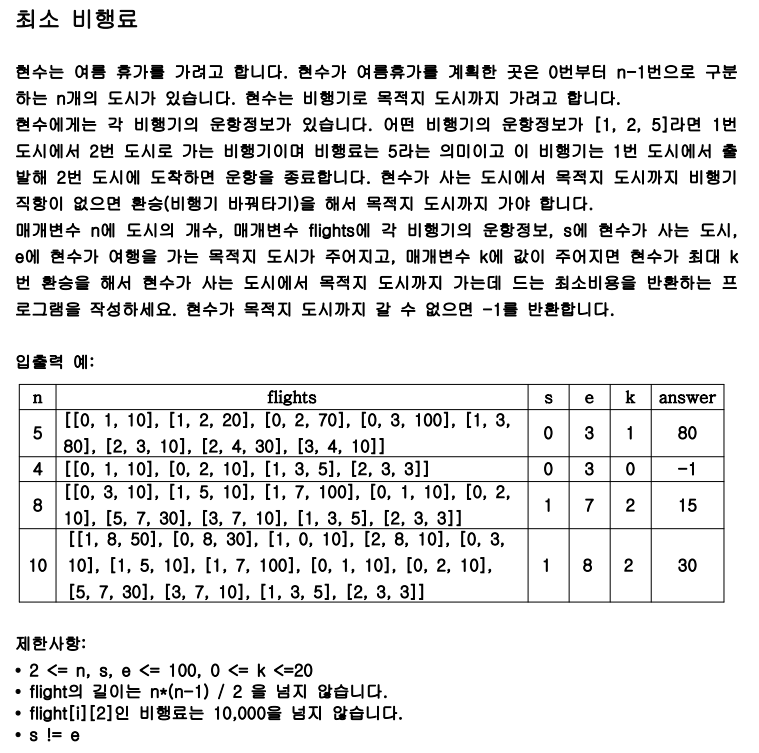

- 처음에는 one-to-all 단순히 다익스트라로 접근하는 문제인 줄 알았는데, 문제 조건에 있는 정해진 ‘환승 횟수’로 제한되어 있기 때문에 레벨 탐색을 해야 한다.
- 다익스트라는 우선순위큐로 무조건 최소비용을 구하는 게 단순 목적인데, 여기서 레벨탐색으로 풀어야 각 레벨(거쳐갈) 당 최소 비용이 구해지기 때문에 주의
- ditance[c_v]가 아닌, c_val 값으로 거리 처리 해야 답이 나온다 왜지 ?
- //직전 Q에서 꺼낸 값 c_val 으로 접근해야 한다.
- for문을 돌면서 내부에서 nx_val 값을 업데이트 하는 중이라
- distance[c_v]로만 접근하게 된다면 직전에 뽑아놨던 c_val 값이 아니라 새로 갱신된 distance[c_v]로 접근하게 되기 때문.
import java.util.*;
//RE 다시 풀이 - 비행기 최소비용
class Solution {
static int[] distance;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<int[]>> graph;
static Queue<int[]> Q;
//solution 함수
public int solution(int n, int[][] flights, int s, int e, int k){
distance = new int[n];//정점개수
graph = new ArrayList<>();
Q = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());//공간ㄱ생성
}
//값 채워넣기
Arrays.fill(distance, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
//데이터 세팅
for(int[] x : flights) {
graph.get(x[0]).add(new int[] {x[1], x[2] });
}
//시작점 세팅
distance[s] = 0;
Q.add(new int[] {s, 0});
int lv = 0;
while(!Q.isEmpty()) {
int len= Q.size();
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) { //하나의 레벨 탐색하는 거임 그 인접 정점들 싹 방문하니까
int[] cur = Q.poll();
int c_v = cur[0];
int c_val = cur[1];
for(int[] nx : graph.get(c_v)) {
int nx_v = nx[0];
int nx_val = nx[1];
if(distance[nx_v] > c_val + nx_val) {
distance[nx_v] = c_val + nx_val;
Q.add(new int[] {nx_v, distance[nx_v]});
}
}
}
lv++;
if(lv > k) break;
}
//break 걸어놓은 상태에서 e 도착점까지의 거리 출력하면 됨
if(distance[e] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) return -1;
return distance[e];
}
//실행 메인
public static void main(String[] args){
Solution T = new Solution();
System.out.println(T.solution(5, new int[][]{{0, 1, 10}, {1, 2, 20}, {0, 2, 70}, {0, 3, 100}, {1, 3, 80}, {2, 3, 10}, {2, 4, 30}, {3, 4, 10}}, 0, 3, 1));
System.out.println(T.solution(4, new int[][]{{0, 1, 10}, {0, 2, 10}, {1, 3, 5}, {2, 3, 3}}, 0, 3, 0));
System.out.println(T.solution(8, new int[][]{{0, 3, 10}, {1, 5, 10}, {1, 7, 100}, {0, 1, 10}, {0, 2, 10}, {5, 7, 30}, {3, 7, 10}, {1, 3, 5}, {2, 3, 3}}, 1, 7, 2));
System.out.println(T.solution(10, new int[][]{{1, 8, 50}, {0, 8, 30}, {1, 0, 10}, {2, 8, 10}, {0, 3, 10}, {1, 5, 10}, {1, 7, 100}, {0, 1, 10}, {0, 2, 10}, {5, 7, 30}, {3, 7, 10}, {1, 3, 5}, {2, 3, 3}}, 1, 8, 2));
}
}🟩 2번. 최소 환승 횟수
package to_0821_5;
//최소 환승 횟수
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
//솔루션 함수
public int solution(int[][] routes, int s, int e){
int answer = 0;
//<역정보, 호선 정보> 로 담는 거임 - 중복없이 Set 사용하여 해당 역을 거치는 호선 정보 담기
HashMap<Integer, HashSet<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
int n = routes.length;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { //i로 찍기
//각 호선별 존재하는 역들 모두 x로 탐색함
for(int x : routes[i]) { //각 i호선에 대한 정보
graph.putIfAbsent(x, new HashSet<Integer>());//키 존재하지 않으면 생성 후 set 담기
graph.get(x).add(i);//생성된 상태에서 방문 역 x로 가는 호선 i를 담기
}
}
Queue<Integer> Q = new LinkedList<>();
//환승횟수 == 레벨
int[] ch = new int[n];//호선 체크용
Q.offer(s);//방문 역 담기
int lv = 0;
while(!Q.isEmpty()) {
int len = Q.size();
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) {//하나의 레벨 안에서
int cur = Q.poll();//현재 방문 역
for(int line : graph.get(cur)) {//현재 방문역을 거치는 호선들 꺼내기
if(ch[line] == 1) continue;//방문한 곳은 그냥 거쳐가고
ch[line]= 1;///방문체크
for(int stop : routes[line]) {
if(stop == e) return lv;
Q.offer(stop);
}
}
}
lv++;
}
return answer;
}
//실행 메인
public static void main(String[] args){
Solution T = new Solution();
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 19}, {2, 7, 8, 13}, {5, 9, 10}, {9, 11, 12, 18}, {13, 14, 15}, {14, 12, 16, 17}}, 1, 12));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{1, 3, 5, 7}, {9, 3, 12}, {6, 5, 8}, {2, 8, 14, 15}, {2, 14, 16}}, 1, 14));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{7, 12},{5, 19},{7, 19},{9, 12, 13},{9, 5, 15}}, 9, 19));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{1, 2, 3, 4, 5},{9, 7, 10},{7, 6, 3, 8}, {5, 11, 8, 12}}, 1, 10));
}
}
🟩 3번. 벽 허물기 | 최소로 벽 허물어서 갈 수 있는 최소 비용
- 0 : 통로, 1:벽
- 최소로 벽을 허물고 갈 수 있는 최소비용
- 다음 cost 배열의 가중치값 선정할 때 {주의}
- 1 ) 다음 정점이 0인 곳으로 가면 +0
- 2 ) 다음 정점이 1인 곳으로 가면 +1
package to_0821_8;
import java.util.*;
//다익스트라로 벽 허물기 - RE
class Solution {
//솔루션 함수
public int solution(int[][] board) {
int n = board.length;
int m = board[0].length;
int[][] cost = new int[n][m];
int[] dx = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = {1, -1, 0, 0};
PriorityQueue<int[]> pQ = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[2] - b[2]);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(cost[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE);//최대값으로 초기화
}
//시작점 초기화
cost[0][0] = 0;//시작점
pQ.add(new int[] {0, 0, 0});
while(!pQ.isEmpty()) { //가중치 적은 애 우선으로 뽑음
int[] cur = pQ.poll();
//cur[0]행 cur[1]열의 가중치는 cur[2] 이다.
if(cur[2] > cost[cur[0]][cur[1]]) continue;
for(int k=0; k<4; k++) {
int nx = cur[0] + dx[k];
int ny = cur[1] + dy[k];
if(nx <0 || ny<0 || nx>= n || ny>=m)continue;
//0이면서 기존 cost보다 더 작은 cur[2]가중치 나타난 경우 얘로 이동처리
if(board[nx][ny] == 0 && cur[2] < cost[nx][ny]) { //그대로 통로 거쳐감
cost[nx][ny] = cur[2];
pQ.add(new int[] {nx, ny, cur[2]});
}else if(board[nx][ny] == 1 && cur[2]+1 < cost[nx][ny]) {
cost[nx][ny]= cur[2]+1;
pQ.add(new int[] {nx, ny, cur[2]+1}); //+1 처리하여 벽 허물기
}
}
}
return cost[n-1][m-1];
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Solution T = new Solution();
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{0, 1, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0}}));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{0, 1, 1, 0},{1, 1, 0, 1},{0, 0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 0}}));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1},{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}}));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}}));
System.out.println(T.solution(new int[][]{{0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1},{1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1},{1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0}}));
}
}
728x90
'알고리즘 이론 [개념] > [개념] 코테 알고리즘 공부 - 시즌 2' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 코테 | 그래프 섹션 - 다익스트라, 위상정렬 문풀 (0) | 2023.08.22 |
|---|---|
| 코테 | 강의 - 너비 우선 탐색 - BFS 섹션 - (2) (0) | 2023.08.18 |
| 코테 | 강의 - 너비 우선 탐색 - BFS 섹션 - (1) (0) | 2023.08.16 |
| 코테 | 강의 - 깊이 우선 탐색 - DFS 섹션 - (2) (0) | 2023.08.14 |
| 코테 | 강의 - 깊이 우선 탐색 - DFS 섹션 - (1) (0) | 2023.08.09 |

